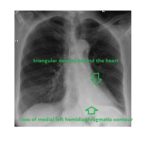
The frontal chest x-ray shows a triangular density behind the heart, silhouetting the medial aspect of the left hemidiaphragm. This appearance is classic for a left lower lobe collapse.
In addition, there is a small pleural effusion on the left, crowding of the ribs on the left and hyperinflation of the right lung.
The cause of left lower lobe collapse in this patient was mucus plugging.
Intrinsic obstruction due to a bronchogenic carcinoma is the most common cause of a left lower lobe collapse in adults. Other causes are mucus plugging, secretions in the bronchus, foreign body obstruction. Rarely mediastinal mass and severe cardiomegaly can lead to obstruction of the left lower lobe bronchus.
Reference: Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology by Brant and Helms, 4th Edition.