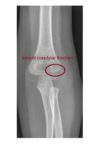
The frontal elbow x-ray shows an undisplaced lateral condylar fracture of the humerus.
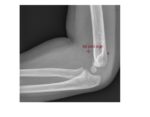
The lateral elbow x-ray shows an elevated anterior fat pad and a visible posterior fat pad, indicative of an effusion (haemarthrosis in the context of trauma).
Why is it important not to miss this injury?
- Second most common elbow fracture in paediatric population.
- High risk of non union/malunion.
- Risk of cubitus valgus and tardy ulnar nerve palsy.
The patient needs orthopedic referral.
Non displaced fractures with less than 2 mm separation is managed conservatively with an above elbow cast and close x-ray follow up whereas displaced fractures with more than 2 mm separation needs operative intervention.
Reference: www.orthobullets.com
